Researchers previously isolated six members of FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT)/ TERMINAL FLOWER 1 (TFL1) gene family and analyzed their expression patterns throughout the vegetative and reproductive developmental stages in Jatropha. Three TFL1 homologues were identified and named JcTFL1a, JcTFL1b and JcTFL1c, respectively. They analyzed the function of an FT orthologue (JcFT) in Jatropha and found that JcFT acted as a flowering promoter.
To elucidate the biological functions of three JcTFL1 genes in the floral initiation of Jatropha, Prof. XU Zengfu and his team of Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) conducted a study to analyze their functions by using a transgenic approach.
The researchers overexpressed JcTFL1 genes in transgenic Arabidopsis and Jatropha, and downregulated JcTFL1b in transgenic Jatropha.
They found that JcTFL1b and JcTFL1c could delay flowering in transgenic Arabidopsis and Jatropha. Both of them could also rescue early flowering and determinate inflorescence phenotype of Arabidopsis tfl1-14 mutant.
While JcTFL1a did not affect the flowering time in transgenic Arabidopsis in both wild type plants and tfl1-14 mutant plants background, it could delay flowering in Jatropha, which might be the results of ectopic expression in Arabidopsis.
In addition, JcTFL1b RNAi Jatropha showed moderately early flowering phenotype, which was similar to MdTFL1 RNAi apple that displayed early flowering phenotypes and extreme reduction of the juvenile phase.
The results showed that JcTFL1 genes played important roles in the regulation of flowering behavior in Jatropha, which would be helpful to improve seed yield of Jatropha.
The study entitled “Three TFL1 homologues regulate floral initiation in the biofuel plant Jatropha curcas” has been published in Scientific Reports.
Contact
Prof. XU Zengfu Ph.D Principal Investigator
Key Laboratory of Tropical Plant Resources and Sustainable Use, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Menglun 666303, Yunnan, China
E-mail: zfxu@xtbg.ac.cn
Tel: +86 691 8713051
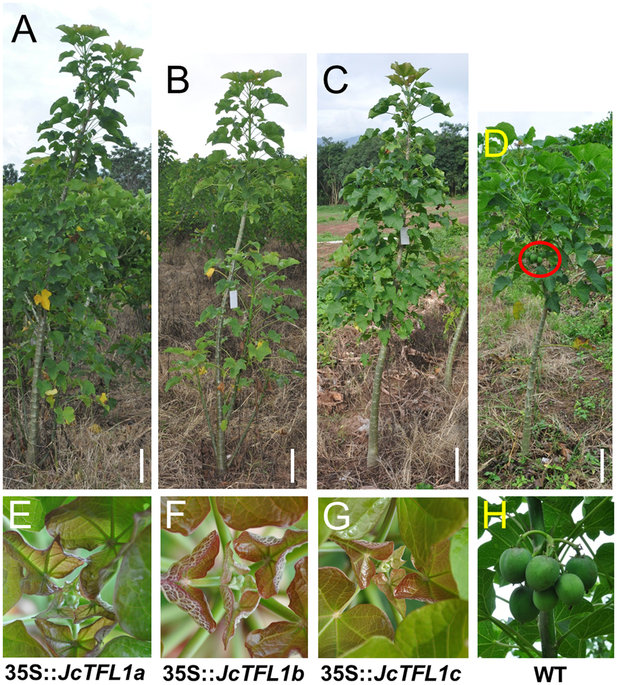
Overexpression of JcTFL1 genes delay flowering in Jatropha.
Transgenic Jatropha overexpressing JcTFL1a (A), JcTFL1b (B) and JcTFL1c (C) have not flowered yet 3 years after plantation in the field.
Wild-type (WT) Jatropha (D) has set fruits about 10 months after plantation in the field;
E, F and G correspond to the developmental stages of shoot apical of transgenic Jatropha shown in (A), (B) and (C), respectively.
(H) The fruits of WT Jatropha shown in (D).
(Images by Li Chaoqiong and FU Qiantang)

