Trichilia americana in the Meliaceae family is native to America, but it was also introduced to the Xishuangbannan Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) in the 1990s. The methanol extract of T. americana showed antifeedant and cytotoxic effects against the Asian armyworm (Spodoptera litura). However, the chemical constituents in this plant species were not reported. Prof. XU Youkai and his team of Xishuangbanna Tropical Botancial Garden (XTBG) have focused on studies of biologically active protolimonoids and limonoids in the Meliaceae family for a few years. As a continuation of research, they isolated ten new (1–10) and two previously reported cedrelone limonoids (deacetylhirtin and hirtin) from the leaves of T. americana. The ten new compounds include americanolides A–D (1–4), 1,2-dihydrodeacetylhirtin (5), 1α-hydroxy-1,2-dihydrodeacetylhirtin (6), 1α-hydroxy-1,2-dihydrohirtin (7), 1α-methoxy-1,2-dihydrodeacetylhirtin (8), 11β-hydroxy-12α-propanoyloxycedrelone (9), and 1α,11β-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydrocedrelone (10). Compound 1 (C31H38O13 )was isolated in the form of colourless crystals. The absolute configuration of compound 1 was confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. All the isolated limonoids were biologically evaluated for their cytotoxic activity against five human tumour cell lines. Compound 11, a major limonoid in this species, exhibited significant cytotoxicity with IC50values ranging from 0.1 to 0.5 μM. The study is the first report on the chemical constituents of T. americana and the enriched diversity of limonoids in the genus Trichilia. 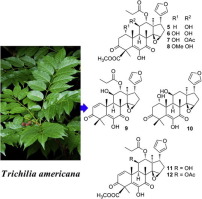
12 cedrelone limonoids isolated from leaves of Trichilia americana (Image by JI Kailong) |

