Jatropha curcas is a perennial deciduous shrub belonging to the family Euphorbiaceae, and is widely distributed in the tropics and subtropics. Jatropha seed content is about 30–40% oil, which is an ideal feedstock for producing biodiesel. However, it has few female flowers, which is one of the most important reasons for its poor seed yield. Increasing the number of female flowers seems critical for the improvement of Jatropha seed yield.
With an aim to find ways to increase the total number and/or the proportion of female flowers of Jatropha, which may result in increased seed yield, Dr. PAN Bangzhen and her teacher Prof. XU Zengfu of Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) investigated the effects of exogenous applications of the plant growth regulator 6-benzyladenine (BA) on the flower, fruit, and seed development of Jatropha.
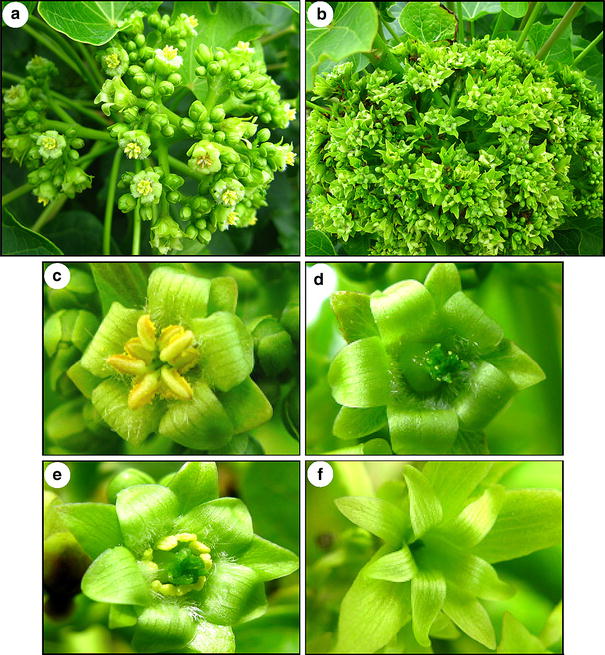
The study found that exogenous application of BA significantly promotes floral development and feminizing effects in Jatropha. BA treatment significantly increased seed yield per inflorescence of Jatropha by increasing the total number of flowers and the proportion of female flowers and the induction of bisexual flowers.
The study indicates that the seed yield of J. curcas can be increased by manipulation of floral development and floral sex expression.
The study entitled “Benzyladenine Treatment Significantly Increases the Seed Yield of the Biofuel PlantJatropha curcas” has been published in Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 30 (2): 166-174. DOI: 10.1007/s00344-010-9179-3
URL: http://www.springerlink.com/content/v5360wx540j671w6/
 (Image by PAN Bangzhen)
(Image by PAN Bangzhen)
Effects of BA treatments on flower development and sex expression of Jatropha. a Inflorescence from control plants. b Inflorescence from BA-treated plants. c-f Flowers of different sexual types from BA-treated plants. c Male flower. d Female flower. e Induced bisexual flower. f Induced asexual flower .
 (Image by PAN Bangzhen)
(Image by PAN Bangzhen)