Plant leaves exhibit a great diversity of forms that can be grouped into two types: simple leaves with a single blade and compound leaves with multiple units termed leaflets. A major question for plant developmental biologists is the molecular mechanism underlying diversity of compound leaf form during evolution.
Medicago truncatula serves as one of the key models of compound leaf development, with leaves having a typical trifoliate pattern. Previous studies have characterized a palmate-like pentafoliata1 (palm1) mutant that developed leaves with five leaflets arranged in a palmate pattern. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the diversification of compound leaf patterns and the regulation of morphogenetic activity remain unknown.
In a study published in the latest issue of Nature Plants, researchers from Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) show that the trifoliate leaf pattern of the model leguminous plant Medicago truncatula is controlled by the BEL1-like homeodomain protein PINNATE-LIKE PENTAFOLIATA1 (PINNA1).
The researchers identified that pinna1 formed five leaflets on compound leaves arranged pinnately, whereas the palm1-pinna1 double mutant produced higher-ordered compound leaves consisting of two orders and up to 13 leaflets in total.
Moreover, transcriptional, in vivo and in vitro biochemical analysis revealed that the BELL homeodomain (BLH) protein PINNA1 collaborates with the C2H2 zinc finger protein PALMATE-LIKE PENTAFOLIATA1 (PALM1) to define the spatiotemporal expression of SINGLE LEAFLET1 (SGL1) and the associated morphogenetic activity during the trifoliate pattern formation.
"Our results demonstrate that PINNA1 is evolutionarily conserved in eudicots," said Prof. CHEN Jianghua, principal investigator of the study.
"This study reveals a framework for trifoliate leaf-pattern formation and sheds light on mechanisms generating diverse leaf forms," added Prof. CHEN.
Contact
CHEN Jianghua Ph.D Principal Investigator
Key Laboratory of Tropical Plant Resources and Sustainable Use, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Menglun 666303, Yunnan, China
E-mail: jhchen@xtbg.ac.cn

Different leaf forms of leguminous plants. (Image by HE Liangliang)
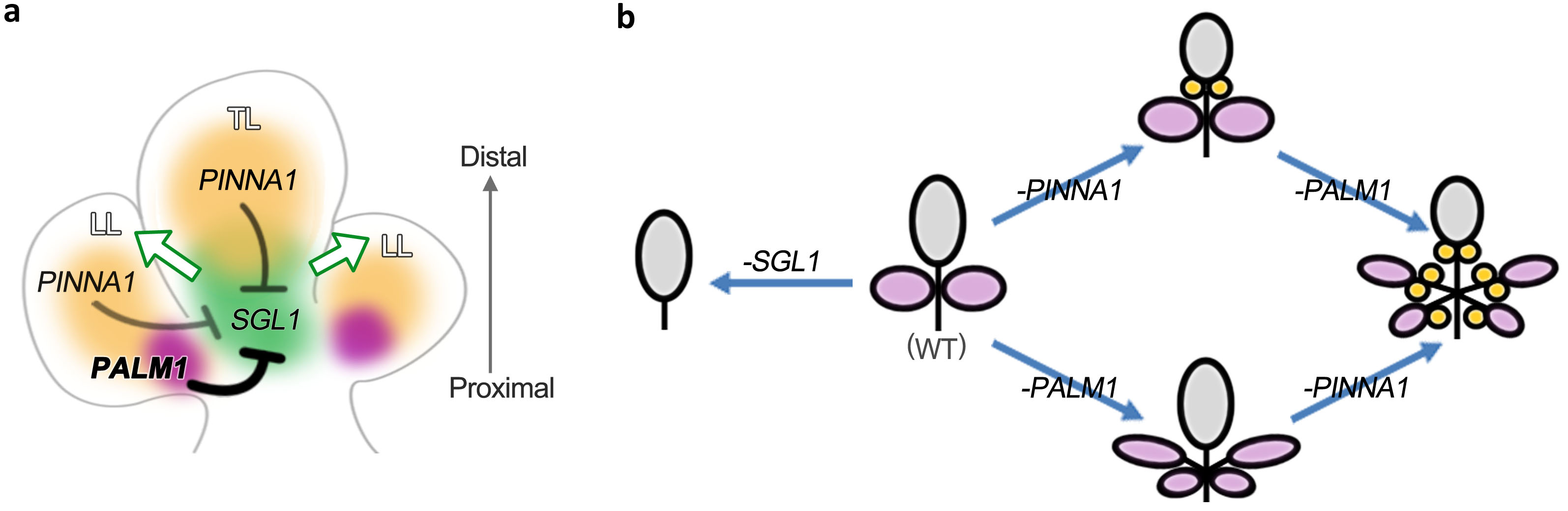
Model for PINNA1, PALM1 and SGL1 action in the pattern formation of compound leaf in M. truncatula. (Image by HE Liangliang)


