Host-killing by hemiepiphytes is an endemic phenomenon in the tropics. Many fig species—keystone plants in tropical forests—have evolved the hemiepiphytic ecotype. However, the benefits and adaptive strategies of their special life history remain poorly understood.
In a study published in New Phytologist, researchers from Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) present that hemiepiphytic figs benefit from lessening phosphorus (P) competition by killing their hosts in the P-deficient tropics, and hemiepiphytic figs can adapt to changing habitats via functional trait trade-offs during the host-killing process.
In order to understand the relationships between P-competition and the host-killing process, the researchers combined an analysis of fig and palm species’ leaf phosphorus (P) content worldwide. They studied the dynamics of leaf functional traits and nutrients in substrates of hemiepiphytic Ficus tinctoria (with both hemiepiphytic and non-hemiepiphytic phenotypes), the host palms (the oil palm, Elaeis guineensis), and non-hemiepiphytic conspecifics at different growth stages.
They found that the leaf P content of both hemiepiphytic figs and their host palms significantly decreased when competing for soil resources. After host death, however, the leaf content of hemiepiphytic figs recovered. With the growth of hemiepiphytic figs, the P-availability in the canopy humus and soil significantly decreased. While competing with their hosts, functional trait trade-offs of hemiepiphytic figs enabled them to adapt to the P-shortage.
“We consider that the P-competition caused by high P-demand of figs may be a general phenomenon, from the common garden to a global scale,” said MO Yuxuan, first author of the study.
The results demonstrate that the high P-demand of figs, P-deficiency in tropics, and zero-distance between hemiepiphytic figs and their host trees lead to intense P competition between them. Hemiepiphytes adapt to changing environments via functioanl trait trade-offs to better utilize limited resources.
“Our results suggest that P-competition is an important factor causing host death, except for mechanically damaging and shading hosts. Our study provides a new perspective on the evolution of host-killing in hemiepiphytes and link this behavior to the widespread P shortages in tropical soils,” said Prof. LIU Wenyao of XTBG.
Contact
LIU Wenyao Ph.D
Key Laboratory of Tropical Forest Ecology, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Mengla, Yunnan 666303, China
E-mail: liuwy@xtbg.ac.cn

Strangler fig tree in XTBG. (Image by MO Yuxuan)

Hemiepiphytic figs at different growth stages. (Image by MO Yuxuan)
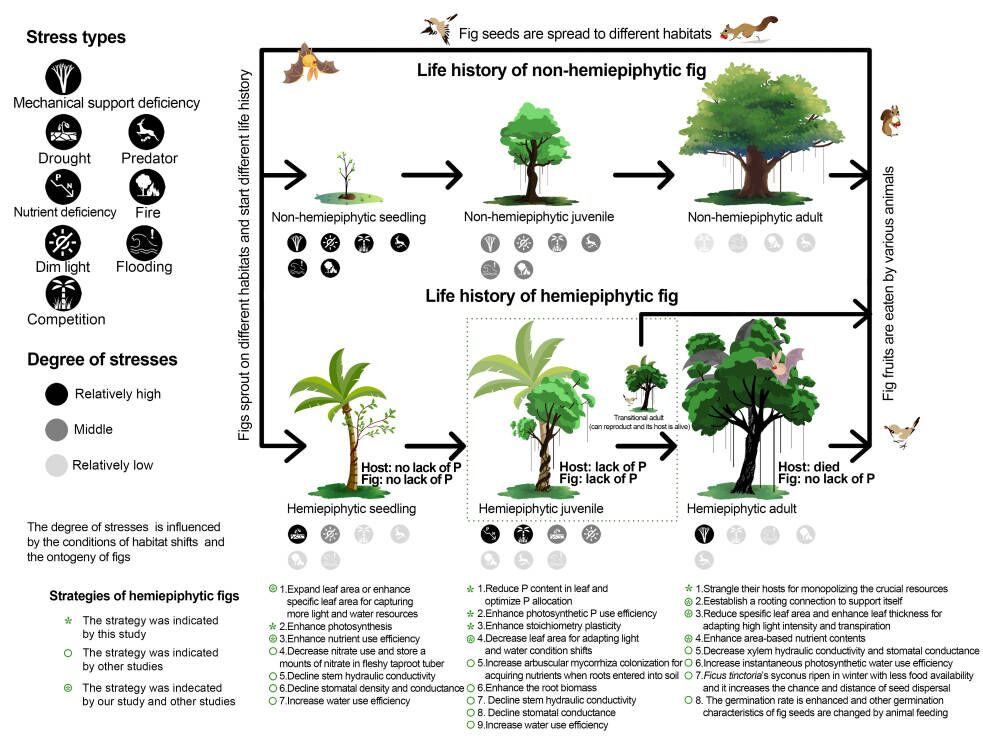
Adaptive strategies of hemiepiphytic figs. (Image by MO Yuxuan)



